iTOL-101
A Potential Breakthrough for Type 1 Diabetes
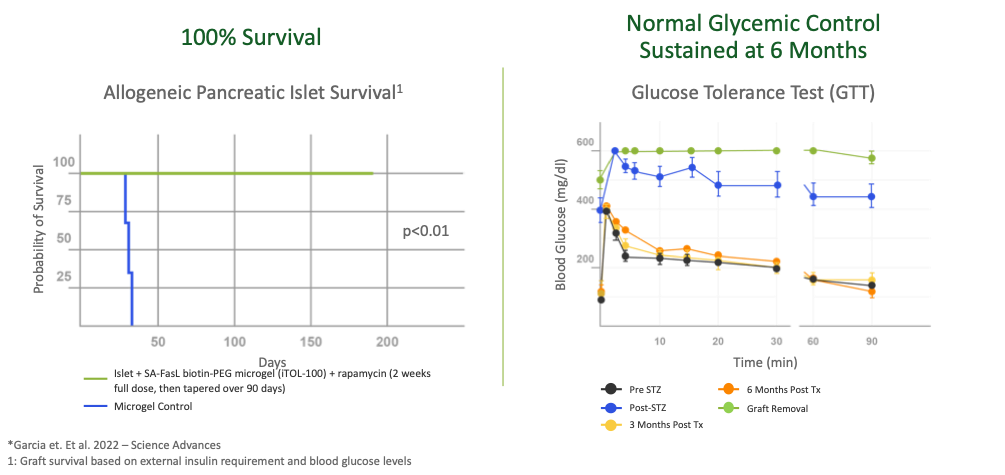
iTOL-101 utilizes allogeneic cadaveric pancreatic islets in combination with iTOL-100 and is being developed as a potential cure for Type 1 Diabetes. In a pre-clinical non-human primate study, insulin-dependent Diabetes, pancreatic islet cells derived from cadavers co-implanted with iTOL-100 exhibited long-term function with control of blood glucose levels and restoration of insulin secretion without the use of chronic immune suppression.
Program Highlights:

Potential to eliminate the need for sustained immunosuppressants

Potential to facilitate
functional engraftment while reducing cell rejection

Compelling efficacy demonstrated in non-human primate studies
Compelling Results Demonstrated in Non-Human Primate (NHP Study Published in Science Advances With iTOL-100
iTOL-100 combined with NHP cadaveric donor islets implanted into an NHP model of Type 1 Diabetes has shown long-term graft function with control of blood glucose levels and restoration of insulin secretion without the use of chronic immune suppression in a preclinical study.
How iTOL-100 is Designed to Work
Even with Insulin Treatment, There Remains a Significant Unmet Need in Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. People with brittle Diabetes frequently experience large swings in blood sugar that can quickly move from too high to too low or vice versa. Severely low blood sugar, called hypoglycemia, can cause sudden and unexpected seizures, coma, heart attacks, and even death.
8.75 million
patients worldwide2
100K – 135K
patients with very severe uncontrolled Type 1 Diabetes characterized as “brittle”4
1.6 million
adult patients over the age of 20 in U.S.3
$800K – $1.7M
average costs of patient treatment
for the payer5
Poor Glucose Control Has Long Term Consequences¹
%
Retinopathy at 18 years (45% are severe)
%
Neuropathy
at 18 years
%
Nephropathy
at 18 years
1: Insulin independence rate from 2007-2010 in 677 islet transplants from Schuetz C, Markmann JF. Islet cell transplant: Update on current clinical trials. Curr Transplant Rep. 2016;3(3):254-263; 2: Ogle, Graham D. 2022, Type 1 Diabetes Estimates in Children and Adults; 3: “Prevalence of Diagnosed Diabetes.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 30 Sept. 2022, www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/diagnosed-diabetes.html; 4: Shamard Charles, MD. “Symptoms of Uncontrolled Diabetes.” Verywell Health, www.verywellhealth.com/uncontrolled-diabetes-symptoms-5120437. Accessed 16 May 2023; 5: merican Diabetes Association. “New American Diabetes Association Report Finds Annual Costs of Diabetes to be $412.9 Billion.” American Diabetes Association, 1 Nov. 2023, https://diabetes.org/newsroom/press-releases/new-american-diabetes-association-report-finds-annual-costs-diabetes-be. Accessed 9 Oct. 2024
Our Technology
Scientific Publications
Our Team

